Have you ever wondered how do credit card transactions work Credit Vault? When you swipe, tap, or click to pay, a seamless process unfolds behind the scenes, involving multiple parties to ensure your payment goes through securely. In this guide, we’ll break down the credit card transaction process step by step, from authorization to settlement. We’ll also explore what is Credit Vault—a secure data protection layer that stores your card information safely—and how it fits into the mix to enhance payment security. Whether you’re a new card user, a small business owner, or someone concerned about fraud, understanding these basics can help you manage your finances smarter. Plus, we’ll cover how digital wallets and tools like Credit Vault make payments faster and safer.
How Do Credit Card Transactions Work?
Credit card payments might seem instant, but there’s a lot happening in those few seconds. The credit card transaction process involves a series of checks and communications between your card, the merchant, and banks. This ensures funds are available, fraud is minimized, and everyone gets paid correctly. Let’s dive into the details.
Step-by-Step Breakdown
Here’s a clear, step-by-step look at how credit cards process payments:
- Authorization: When you swipe, tap, or enter your card details online, the merchant’s point-of-sale system or website captures your card information. This data is sent to a payment processor, which acts as a middleman. The processor forwards it to the card network (like Visa or Mastercard) and then to your issuing bank for approval.
- Verification: Your issuing bank quickly checks several things: Is the card valid? Is there enough available credit? Are there any signs of fraud, like unusual location or amount? This step uses advanced algorithms and sometimes even your phone for two-factor authentication.
- Approval/Decline: If everything checks out, the bank approves the transaction and sends a confirmation back through the chain. If not—maybe due to insufficient funds or suspected fraud—it’s declined, and you’ll see an error message right away.
- Settlement: Once approved, the transaction isn’t fully done. The merchant batches up all approved sales at the end of the day and submits them for settlement. The acquiring bank (the merchant’s bank) requests funds from your issuing bank via the card network.
- Billing: Finally, the charge posts to your credit card statement, usually within a few days. You’ll see it as a pending charge first, then as a confirmed one.
This entire authorization and settlement in credit cards happens in real time for the approval part—often in just 1-2 seconds—but full settlement can take a bit longer. Tools like Credit Vault can streamline this by securely storing your info for quicker future use.
Who Are the Key Players in a Credit Card Transaction?
Every credit card transaction is like a well-orchestrated team effort. Understanding the roles helps demystify the process and highlights where security comes in. Here’s who’s involved:
- Cardholder: That’s you! You initiate the payment with your credit card, providing the details needed to start the flow.
- Merchant: The business or online store accepting your payment. They use terminals or gateways to capture and send your card data securely.
- Payment Processor: Companies like Stripe or Square handle the technical routing. They encrypt data and communicate between the merchant and the card network, ensuring compliance with standards like PCI DSS for secure credit card payments.
- Card Network: Visa, Mastercard, American Express, or Discover. They set the rules, facilitate communication, and sometimes handle fraud detection.
- Issuing Bank: Your credit card company (e.g., Chase or Capital One). They issue the card, manage your credit limit, and decide on approvals based on your account status.
- Acquiring Bank: The merchant’s bank, which receives the funds and deposits them into the business’s account after deducting fees.
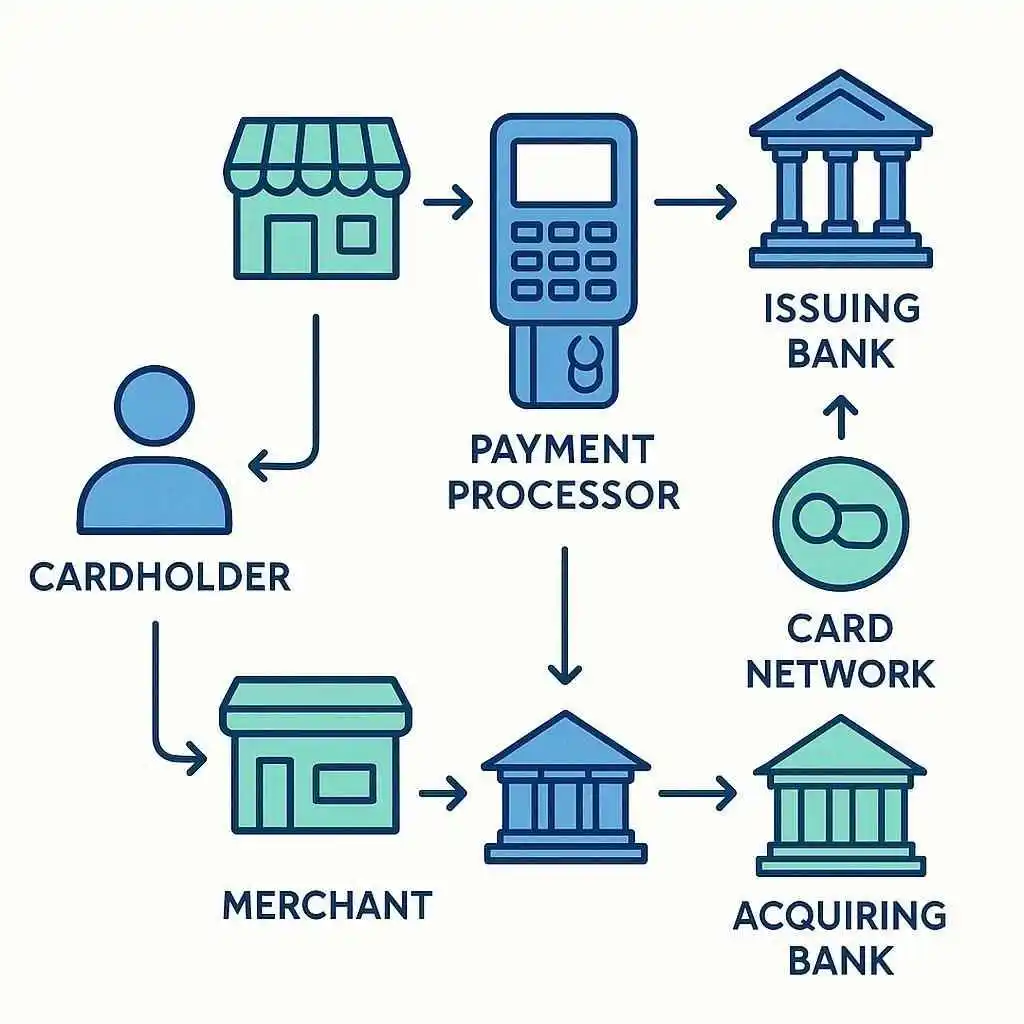
These players interact swiftly: The merchant sends data to the processor, which pings the network, then the issuing bank verifies, and the acquiring bank settles. This chain keeps things efficient, but it also introduces points where data protection is crucial—enter concepts like Credit Vault for added security.
What Is Credit Vault and How Does It Fit In?
If you’re asking how do credit card transactions work Credit Vault, it’s worth explaining this tool first. Credit Vault refers to a secure digital storage system, often called a credit card vault, that acts as a data protection layer for your payment information. Think of it as a fortified safe for your card details, used by merchants, apps, or financial services to store data without exposing it during every transaction.
In the credit card transaction process, Credit Vault fits in by replacing your actual card number with a token—a unique code that represents your info without revealing it. This tokenization reduces risks at checkout. For example, when you save your card in an online store or app, Credit Vault encrypts and stores the data offsite, often with military-grade security. It may integrate biometric verification, like fingerprint or face ID, for added protection.
Unlike traditional methods where your full card details are shared each time, Credit Vault minimizes exposure to breaches. It’s especially useful for recurring payments, like subscriptions, where you don’t want to re-enter info repeatedly. Overall, it enhances how digital wallets work by focusing on credit vault payment security and fraud prevention.
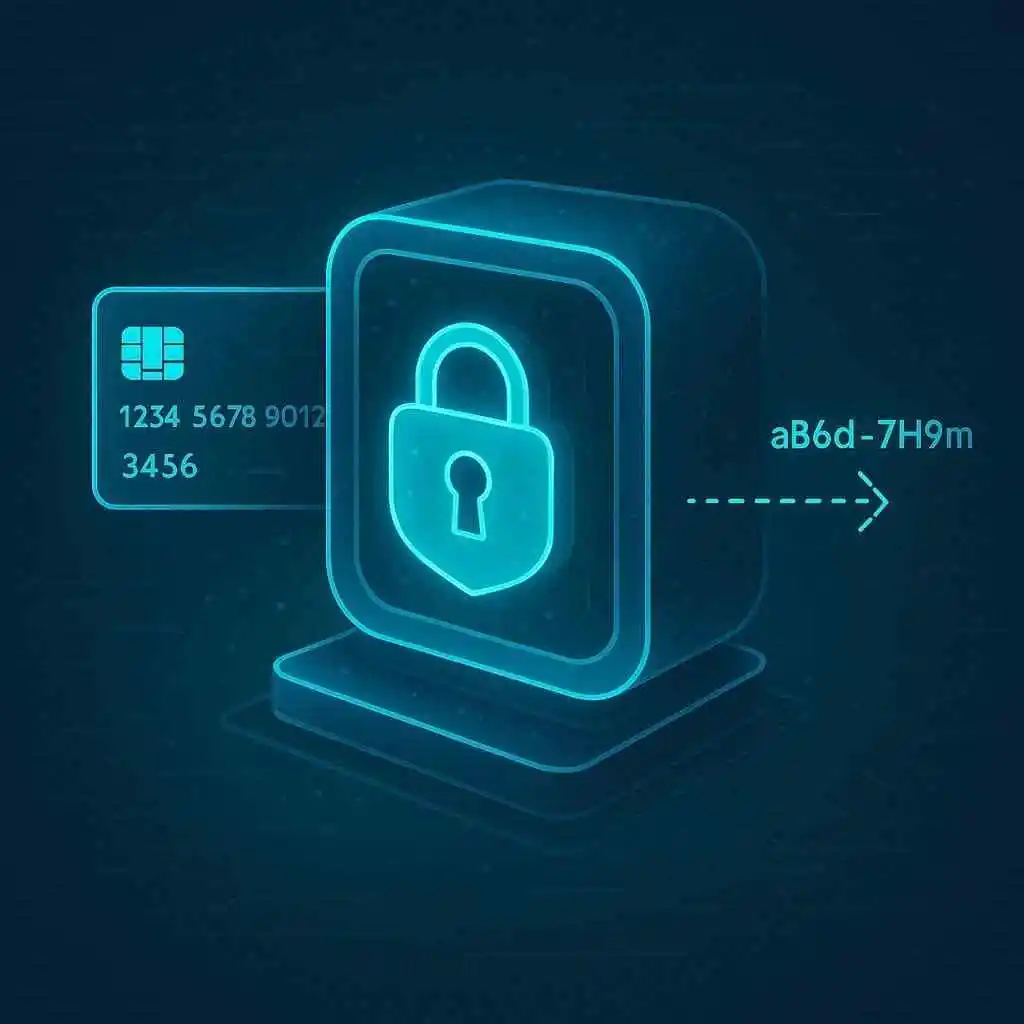

How Credit Vault Enhances Transaction Security
Security is a top concern in credit card payments, with data breaches making headlines. Credit Vault addresses this by adding layers of protection. Here’s how it boosts secure credit card payments:
- Encrypts Your Card Info During Transactions: Sensitive data like your card number and CVV are encrypted, making it unreadable to hackers even if intercepted.
- Prevents Card Skimming or Data Theft: By storing info in a secure vault instead of on merchant servers, it reduces vulnerability to skimmers at physical terminals or online hacks.
- Works with Contactless/NFC Payments: Supports tap-to-pay tech, ensuring quick transactions without compromising safety.
- Supports Tokenization: Replaces real card numbers with secure tokens, so merchants never handle your actual details—cutting down on fraud risks.
- May Integrate with Apple Pay or Google Pay for Ease: Many Credit Vault systems work seamlessly with popular digital wallets, adding convenience while maintaining high security standards.
Using Credit Vault explained this way, it’s clear how it acts as a shield in the payment processor and issuing bank ecosystem, giving you peace of mind.
Credit Card Processing Timeline: How Long Does It Take?
While approvals feel instant, the full cycle has stages with varying durations. Here’s a breakdown in a simple table:
| Stage | Duration | What Happens |
|---|---|---|
| Authorization | Instant (1–2 seconds) | Initial check and approval/decline from your bank. |
| Settlement | 1–3 business days | Funds transfer from your bank to the merchant’s. |
| Posting to Account | Up to 5 days | Charge appears on your statement; may show as pending first. |
Why the delays? Authorization is real-time to prevent overspending, but settlement involves batch processing and fee deductions. Credit card holds or pending charges occur during authorization—your bank reserves funds temporarily, even if the final amount (like at a gas pump) adjusts later. This timeline ensures accuracy and allows time for disputes. With Credit Vault, repeat transactions can skip some steps, speeding things up without sacrificing security.
Common Questions About Credit Card Payments
What happens if a credit card transaction is declined?
It could be due to insufficient credit, expired card, or fraud alerts. The merchant gets a code explaining why, and you might need to contact your bank or try another payment method. No funds are transferred in a decline.
Can I reverse a transaction after it’s approved?
Yes, through a chargeback or refund. Contact the merchant first for a refund; if unresolved, dispute with your issuing bank within 60 days. It’s not instant—investigations take time.
Is it safe to store my card in Credit Vault?
Absolutely, if it’s a reputable system. Credit Vault uses encryption and tokenization for credit card data protection, far safer than storing on unsecured sites. Always check for PCI compliance.
What’s the difference between authorization and settlement?
Authorization is the quick “yes/no” check on funds and validity. Settlement is the actual money movement, happening later to finalize the payment.
Read More- Can I Exclude a Credit Card from Chapter 13
Conclusion
In summary, credit card transactions work through a secure flow of authorization, verification, approval, settlement, and billing—involving cardholders, merchants, processors, networks, and banks. It’s a process designed for speed and safety, but understanding it empowers you to spot issues like fraud early. Tools like Credit Vault elevate this by providing robust data protection, tokenization, and integration with digital wallets, making everyday payments more convenient and secure.
Whether you’re a student budgeting your first card or a small business owner handling sales, grasping these steps helps you stay in control. Ready to level up? Explore secure tools like Credit Vault for better protection, or dive into more credit card security tips on our blog. Manage wisely, and your finances will thank you!

Emma Rose is a U.S.-based personal finance writer and a regular contributor at Cardix.us. She focuses on topics like credit cards, credit scores, and everyday money management. Emma’s writing makes complex financial concepts simple and practical, helping readers make smarter credit and spending decisions with confidence.


